Shed Ventilation: How-to and Things to Consider
Proper airflow management in outdoor storage spaces is essential for maintaining a healthy environment. Many garden building owners overlook this critical aspect, which can lead to significant problems over time. Effective air circulation prevents moisture buildup and protects valuable contents.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental principles of air movement in garden structures. It explains why adequate airflow is crucial for preserving both the building’s integrity and the items stored inside. Different materials like wood and metal require specific approaches to ensure optimal performance.
The resource provides practical advice on assessing current conditions and identifying signs of poor air quality. Readers will discover various solutions suitable for different budgets and requirements. From simple passive systems to more advanced mechanical options, there are choices for every situation.
Step-by-step installation guidance helps property owners implement improvements effectively. Whether working with new constructions or existing garden buildings, the information supports informed decision-making. Regular maintenance ensures long-term performance and protection.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Key Takeaways
- Proper airflow prevents moisture damage and maintains structural integrity
- Different building materials require tailored ventilation approaches
- Assessing current conditions helps identify necessary improvements
- Various solutions exist for different budgets and requirements
- Regular maintenance ensures optimal long-term performance
- Both passive and mechanical systems offer effective options
- Correct installation is crucial for system effectiveness
Introduction to Shed Ventilation
Adequate air exchange in outdoor constructions is vital for structural preservation. Many property owners underestimate this fundamental aspect of building maintenance. Proper atmospheric management prevents numerous issues before they begin.
Understanding the Importance of Air Flow
Effective air movement serves as the cornerstone of a healthy storage environment. Stagnant atmospheric conditions can harbour excessive moisture and heat. These elements threaten both the building’s integrity and its contents.
Different construction materials respond uniquely to environmental factors. Wooden structures naturally permit some air movement through construction gaps. Metal buildings require more deliberate planning due to rapid heat absorption.
During summer months, internal temperatures can soar 20-25 degrees above external conditions. This thermal buildup potentially damages stored items from plastics to gas containers. Proper atmospheric control regulates these extremes effectively.
Impact on Shed Longevity and Performance
The long-term benefits of proper air circulation extend beyond immediate concerns. Consistent moisture prevention significantly extends a structure’s operational lifespan. Building materials remain stable and functional for years longer.
Health and safety considerations are equally important when storing chemicals or combustible liquids. Adequate fresh air intake prevents harmful fume accumulation. This protects users from potential respiratory issues or skin irritation.
For many situations, simple measures like opening doors or windows provide sufficient air exchange. However, specific storage needs or challenging climates may require enhanced solutions. Recognising signs of poor atmospheric quality helps determine appropriate actions.
Benefits of Proper Shed Ventilation
Implementing effective airflow systems in garden buildings yields substantial protective advantages for both the structure and its contents. These systems maintain optimal conditions that prevent numerous common issues affecting outdoor storage spaces.
Preventing Moisture and Condensation
Proper air movement actively combats humidity accumulation. Continuous atmospheric exchange replaces damp interior air with drier external air.
This process maintains humidity levels below the critical 60% threshold. Condensation occurs when warm, moist air meets cold surfaces.

Water droplets form on walls, ceilings, and stored possessions. Adequate airflow eliminates the temperature differentials that cause this phenomenon.
“The greatest threat to any building is not time, but uncontrolled moisture that silently compromises structural integrity.”
Maintaining Structural Integrity and Stored Items
Excess moisture threatens building components through multiple mechanisms. Wood rot weakens timber frames, while metal parts suffer corrosion.
Visible indicators signal underlying problems requiring attention. Recognising these signs early prevents extensive damage.
| Damage Indicator | Structural Impact | Content Damage | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Condensation on surfaces | Peeling paint, wood warping | Tool rust, mildew growth | Continuous air exchange |
| Musty odours | Mould in wall cavities | Fabric deterioration | Humidity control below 60% |
| Swelling wood | Door/window misalignment | Furniture deformation | Proper atmospheric circulation |
| Visible mould growth | Timber decay acceleration | Health hazard creation | Regular air quality maintenance |
Stored items receive equal protection from proper air management. Tools, equipment, and furniture avoid humidity-related deterioration.
Health benefits emerge from preventing mould and mildew proliferation. These organisms can cause respiratory issues when airborne.
Economic advantages become apparent through avoided repair costs. Relatively modest investments in airflow systems prevent expensive structural repairs and content replacement.
Shed Ventilation: How-to and Things to Consider
Systematic evaluation of air movement patterns provides the foundation for making informed decisions about necessary enhancements. This process ensures any modifications effectively address specific needs.
Evaluating Your Building’s Current Air Flow
Begin by examining existing openings like windows and vents. Note their positions and effectiveness in promoting air exchange throughout the space.
Look for restricted airflow areas where stale air accumulates. Use a hygrometer to measure humidity levels objectively. Readings consistently above 60% indicate insufficient air movement.
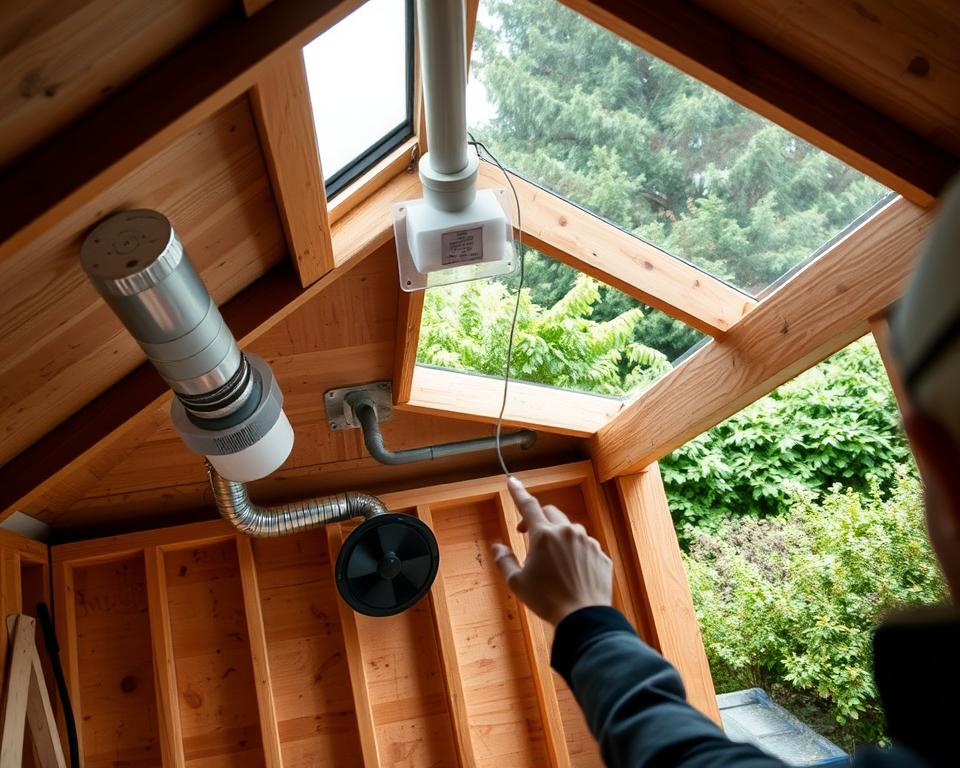

Watch for warning signs like condensation patterns or musty odours. Evidence of warped wood or rust formation suggests moisture problems requiring immediate attention.
Key Factors to Consider Before Installation
The building’s size significantly influences ventilation requirements. Structures larger than 14×18 feet typically need more extensive systems. Consider the intended use – workshops storing chemicals require more air exchange than general storage.
Local climate patterns affect seasonal needs. Winter conditions demand special consideration for temperature control and moisture management. Position the gable end to face prevailing winds for optimal performance.
Site-specific factors include available shade and surrounding vegetation. These elements impact heat gain and airflow patterns. Light-coloured roof finishes help maintain cooler temperatures.
“Measure twice, cut once – proper planning prevents poor performance in atmospheric management systems.”
Most small to medium buildings function well with simple passive systems. Vents on opposite sides create effective cross-ventilation. Always measure dimensions accurately before selecting components.
Ventilation Options and Solutions
Multiple approaches exist for managing air quality in garden structures, each with distinct advantages. Property owners can choose between systems that operate naturally or require power assistance.

Passive vs Mechanical Ventilation Methods
Passive systems utilise natural forces like wind and thermal dynamics. These options function continuously without electricity or moving components.
Mechanical solutions incorporate fans or powered units for enhanced performance. They offer precise control but require energy sources and occasional maintenance.
Comparing Wall Vents, Ridge Vents and Turbine Options
Wall vents provide simple, cost-effective solutions for basic airflow needs. Their louvred design prevents insect entry while allowing air passage.
Ridge vents installed along the roof peak effectively release rising hot air. This option works particularly well when paired with lower intake vents.
Turbine vents use wind power to actively draw air from the interior space. Their spinning action creates vacuum effects that enhance natural convection currents.
Window placements and specialised roof openings offer additional choices. The optimal selection depends on building size, local climate, and specific usage requirements.
Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
Maintaining effective air circulation involves regular upkeep and seasonal adjustments. Proper implementation ensures long-term performance of any airflow system in garden structures.
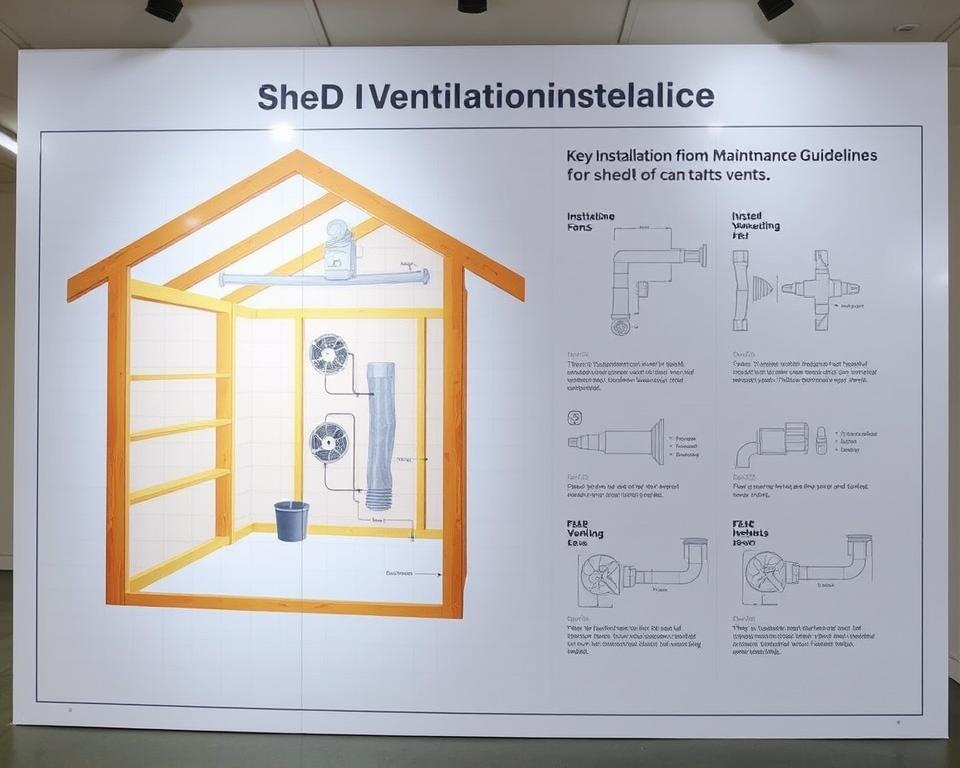
Step-by-Step Installation Tips for Different Shed Types
Wall vent fitting begins with precise measurement and marking. Cut openings using appropriate tools for the building material.
Secure frames with screws or nails before applying weatherproof caulking. This prevents air leaks and water infiltration around edges.
Roof installations require particular attention to weather sealing. Ridge vents need continuous slots along the peak without compromising structural integrity.
For turbine models, select locations with maximum wind exposure. Verify that rotating mechanisms spin freely after installation.
Regular Maintenance to Ensure Efficient Air Flow
Seasonal inspections identify debris blocking vents or screens. Remove leaves and nests that obstruct airflow pathways.
Check seals around windows and doors annually. Repair any gaps that might cause drafts or moisture entry.
Complementary measures enhance system performance. Keep vegetation clear of walls and maintain space between stored items and surfaces.
Moisture absorption materials like silica gel help control humidity levels. Proper drainage around the foundation prevents ground moisture seepage.
Conclusion
A well-considered approach to air management protects garden buildings from seasonal challenges. This guide demonstrates that effective solutions exist for every type of outdoor structure and budget constraint.
Property owners can maintain excellent conditions through regular monitoring and swift issue resolution. The strategies outlined enable identification of problems before significant damage occurs to either the building or its contents.
Seasonal preparation, particularly during colder months, ensures consistent protection throughout the year. By implementing appropriate systems and maintenance routines, garden buildings remain dry, comfortable, and structurally sound for extended periods.
FAQ
Why is air circulation important for a garden building?
Proper air circulation is vital because it helps control internal humidity levels. Without it, moisture accumulates, leading to condensation. This dampness can damage the structure and any items stored inside.
What are the main benefits of installing vents in a log cabin?
Installing vents prevents the build-up of excess moisture, which protects the wood from rot and mould. It also helps regulate temperature, keeping the interior cooler in summer and reducing heat damage.
How can one tell if a garden shed needs better airflow?
Signs include a musty smell, visible mould growth, or condensation on windows and walls. If the interior feels damp or stuffy, it strongly indicates that the current ventilation is insufficient.
What is the difference between passive and mechanical ventilation?
Passive ventilation uses natural forces like wind and thermal uplift through features like ridge vents or wall vents. Mechanical systems employ fans to actively move air, offering more control but requiring energy.
Where is the best place to install vents?
For effective cross-ventilation, it is best to place vents on opposite walls. Positioning them high and low encourages a stack effect, allowing hot air to escape from the top while drawing in cooler air from below.
Can windows provide enough airflow on their own?
While windows help, they are often not sufficient for continuous air exchange, especially when closed. For optimal results, they should be used in conjunction with dedicated vents to ensure a consistent flow.
What maintenance does a ventilation system require?
Regular checks are essential. One should inspect vents for blockages like leaves or debris and clean them periodically. For mechanical fans, ensure they are functioning correctly and free from dust.
Are there specific considerations for winter?
Yes, ventilation remains crucial in colder months to manage humidity from sources like damp storage items. Adequate airflow prevents condensation from freezing inside, which could cause damage.

