How to Build a Shed Base on Uneven Ground
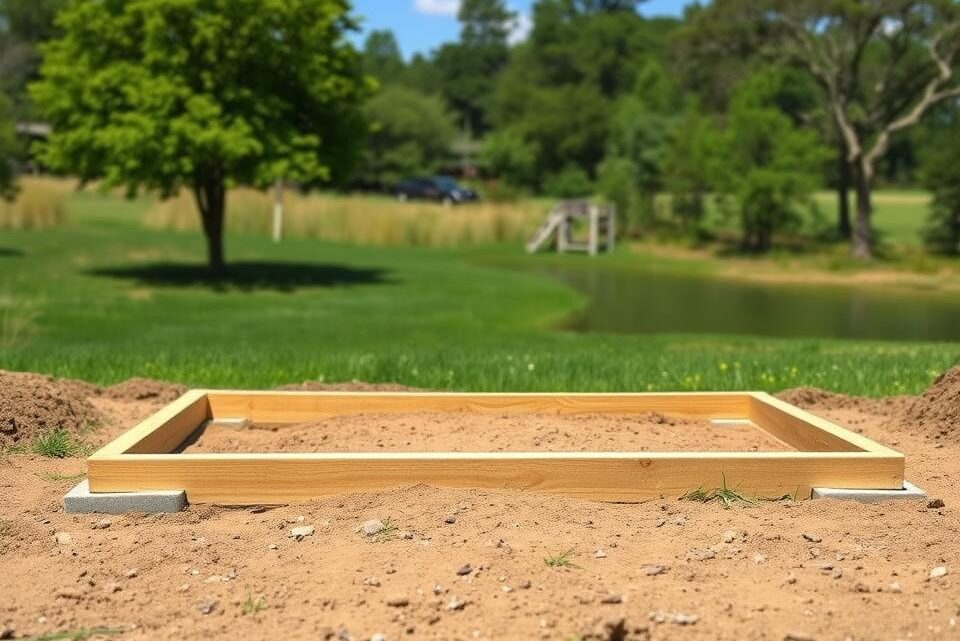

Building a garden shed foundation on uneven ground presents unique challenges for DIY enthusiasts and homeowners. A robust shed base is crucial for ensuring stability, longevity, and protection against ground moisture and structural damage.
Uneven terrain can compromise the structural integrity of your garden shed if not properly addressed. Selecting the right foundation method becomes essential when dealing with sloped or irregular landscapes. Professional preparation will help you create a level, secure base that supports your shed effectively.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the critical steps of constructing a shed base on challenging ground, providing practical techniques to transform an uneven surface into a solid foundation for your outdoor storage solution.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Key Takeaways
- Understand ground conditions before starting construction
- Select appropriate foundation type for specific terrain
- Implement proper drainage solutions
- Use precise levelling techniques
- Prioritise structural stability and long-term durability
Understanding Site Preparation for Uneven Ground
Successful shed construction begins with meticulous site preparation. Uneven ground presents unique challenges that require careful assessment and strategic planning. Proper site preparation ensures a stable, long-lasting foundation that can withstand various environmental conditions.
Effective site preparation involves several critical steps that homeowners must carefully consider before breaking ground on their shed project.
Assessing Ground Conditions
Ground condition analysis is the cornerstone of successful site preparation. Homeowners should conduct a thorough inspection of the proposed building area, looking for potential issues such as:
- Underground water sources
- Rock formations
- Existing vegetation
- Natural drainage patterns
“Understanding your land is the first step to a successful construction project.” – Professional Landscaping Expert
Measuring Slope Gradient
Slope gradient plays a crucial role in site preparation. Different slopes require specific techniques to create a level foundation. Measurement methods include:
- Using a carpenter’s level
- Employing a digital inclinometer
- Creating a simple water level
Professional builders recommend a maximum slope gradient of 10 degrees for shed foundations to ensure stability and proper drainage.
Identifying Soil Types
Soil types significantly impact site preparation and foundation design. Different soil compositions require unique approaches:
| Soil Type | Drainage Characteristic | Foundation Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Clay | Poor drainage | Raised foundation |
| Sandy | Excellent drainage | Compact base |
| Loam | Moderate drainage | Standard foundation |
Understanding your specific soil type will help you make informed decisions about site preparation, ensuring a robust and durable shed foundation.
Essential Tools and Materials Needed
Building a sturdy shed base on uneven ground requires careful preparation and the right shed base tools. DIY enthusiasts will need a comprehensive set of construction materials and equipment to ensure a successful project.
Your DIY equipment arsenal should include several key tools for creating a solid foundation:
- Measuring Tools
- Laser level
- Tape measure
- Spirit level
- Digging and Levelling Equipment
- Shovel
- Pickaxe
- Rake
- Wheelbarrow
For construction materials, you’ll want to gather:
- Gravel
- Concrete blocks
- Timber bearers
- Landscape fabric
- Hardcore substrate
Professional DIY enthusiasts recommend investing in quality shed base tools that will make the job easier and more precise. A transit level or digital inclinometer can be particularly helpful for measuring ground gradients accurately.
Pro tip: Always check your tools and materials before starting the project to avoid unnecessary interruptions.
Selecting the right DIY equipment and construction materials will set the foundation for a stable and long-lasting shed base, even on challenging uneven terrain.
How to Build a Shed Base on Uneven Ground
Constructing a shed base on uneven ground requires careful planning and precise ground preparation. Successful shed base construction depends on meticulous techniques that create a stable and level foundation. Homeowners can transform challenging terrain into a solid base with the right approach.
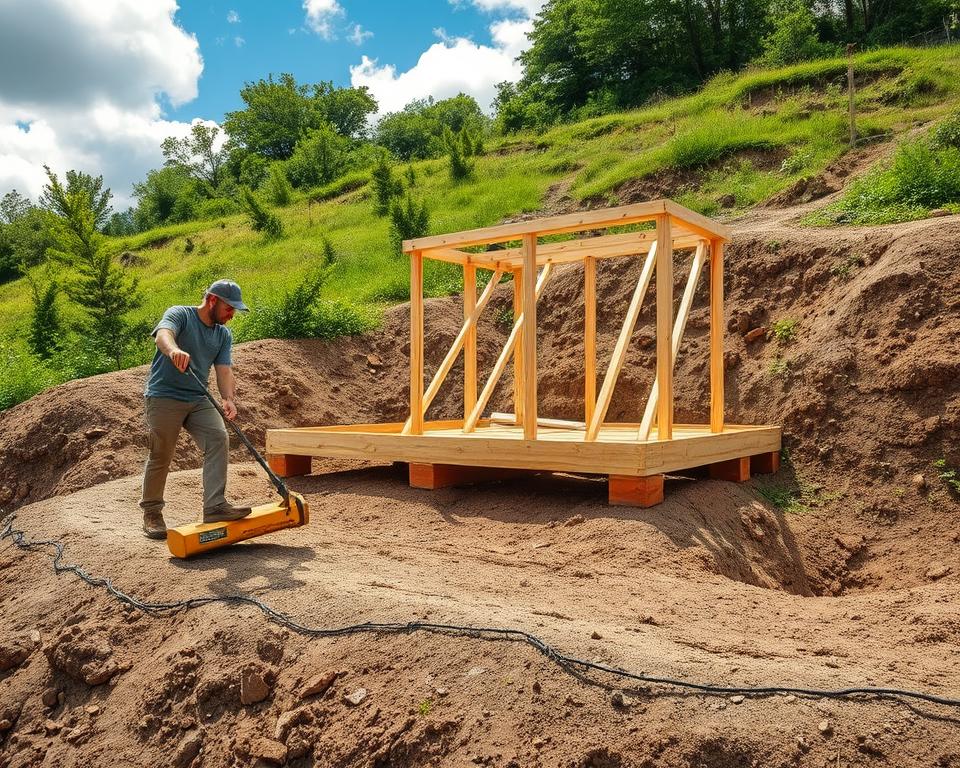

Preparing the ground for your shed involves several critical steps that ensure long-term stability and durability. Levelling techniques are essential for creating a reliable foundation that can withstand various environmental conditions.
Marking Out the Area
Begin your shed base construction by precisely marking the intended area. Use the following steps:
- Measure the exact dimensions of your planned shed
- Use wooden stakes and string to outline the perimeter
- Verify square corners using the 3-4-5 triangulation method
- Check measurements multiple times for accuracy
Clearing and Excavating
Ground preparation requires thorough clearing and strategic excavation:
- Remove grass, weeds, and organic materials
- Clear rocks, roots, and debris from the site
- Use a spirit level to assess ground slope
- Create a gradual, even surface for foundation installation
Creating Level Reference Points
Establishing level reference points is crucial for successful shed base construction. Utilise professional levelling techniques to ensure a stable foundation:
| Technique | Purpose | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Level | Precise horizontal measurements | Laser level, tripod |
| Water Level | Accurate ground levelling | Clear tubing, water |
| Transit Level | Professional-grade ground assessment | Optical level, measuring staff |
Pro tip: Always double-check your measurements and take your time during ground preparation to achieve the best results.
Choosing the Right Foundation Type
Selecting the appropriate shed foundation options is crucial for creating a stable and long-lasting structure on uneven ground. Different foundation types offer unique advantages depending on your specific terrain and project requirements.
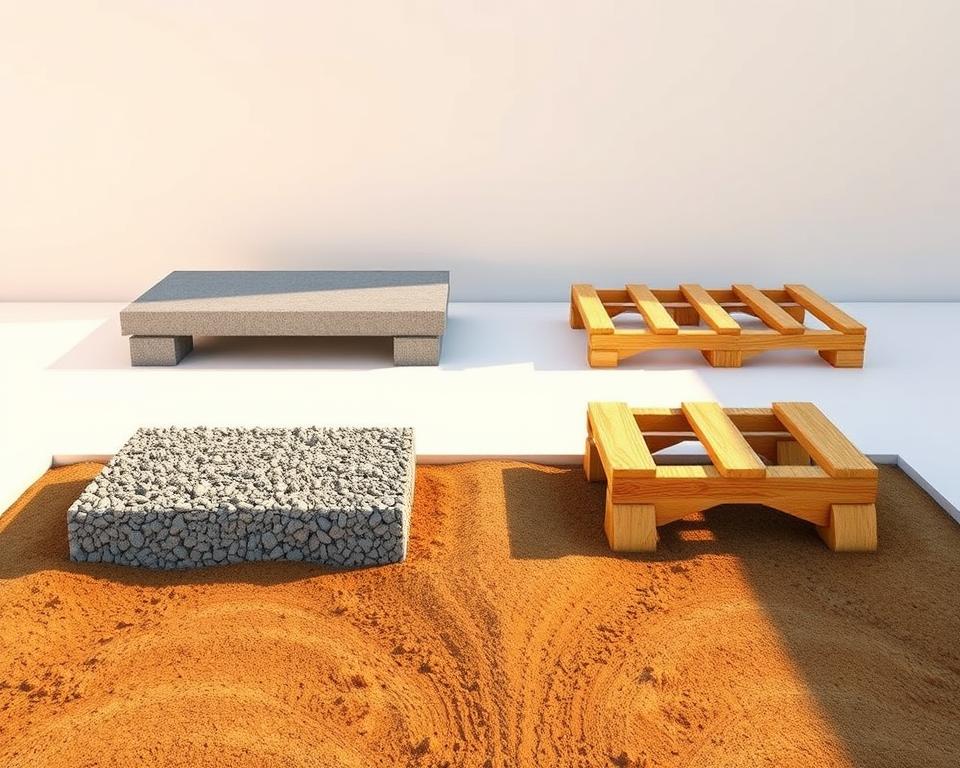
When considering shed foundation options, you’ll typically encounter three primary choices:
- Concrete base
- Concrete block foundation
- Timber frame base
Each foundation type presents distinct characteristics that can impact your shed’s durability and performance:
| Foundation Type | Pros | Cons | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete Base | Extremely stable, long-lasting | Higher cost, complex installation | Large sheds, permanent structures |
| Concrete Block | Moderate cost, good stability | Requires precise levelling | Medium-sized sheds on slightly uneven ground |
| Timber Frame | Lightweight, easy installation | Less durable in wet conditions | Small sheds, DIY projects |
Your choice of a timber frame or concrete base depends on several critical factors, including ground slope, budget, and intended shed usage. Professional assessment of your specific site conditions can help determine the most suitable foundation type.
Factors to evaluate include ground gradient, soil composition, drainage patterns, and the shed’s intended purpose. Consulting with a local landscaping professional can provide tailored advice for your specific location.
Installing a Concrete Block Foundation
Creating a stable shed base on uneven ground requires careful planning and precise installation of a concrete block foundation. This crucial step ensures your shed remains level, secure, and protected from ground moisture and shifting terrain.
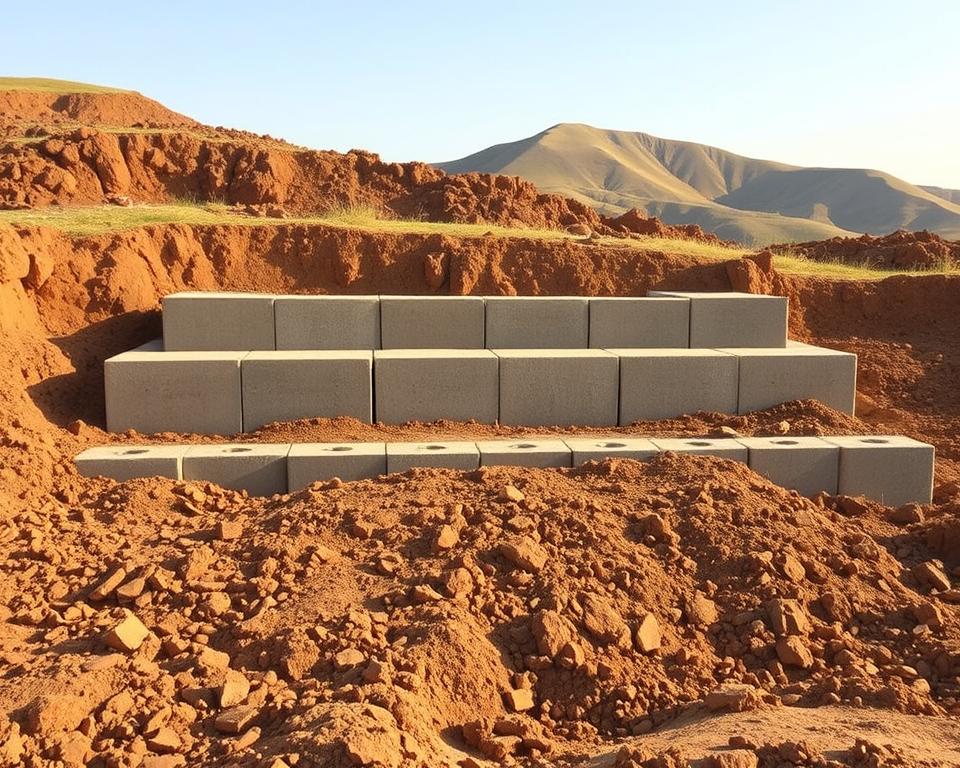

A well-constructed concrete block foundation provides critical shed base support for structures built on challenging landscapes. The process involves strategic placement and precise levelling to create a stable platform.
Setting Corner Blocks Accurately
When establishing your concrete block foundation, start with the corner blocks as your primary reference points. These blocks must be positioned with extreme precision to ensure the entire shed base remains level.
- Measure diagonal distances to confirm square alignment
- Use a spirit level to check horizontal positioning
- Ensure each corner block sits firmly on compacted ground
Mastering Levelling Techniques
Levelling blocks requires patience and careful adjustment. Different ground conditions demand specific approaches to create a uniform surface.
- Use gravel or sand as a base layer for initial levelling
- Employ levelling blocks to compensate for ground variations
- Check level in multiple directions using a long spirit level
Adding Support Blocks
Support blocks are essential for distributing weight evenly across your shed foundation. Place intermediate blocks between corners to prevent sagging and enhance structural integrity.
Pro tip: Space support blocks no more than 1.2 metres apart for maximum stability.
By following these detailed steps, you’ll create a robust concrete block foundation that provides reliable shed base support on even the most challenging terrain.
Building a Timber Frame Base
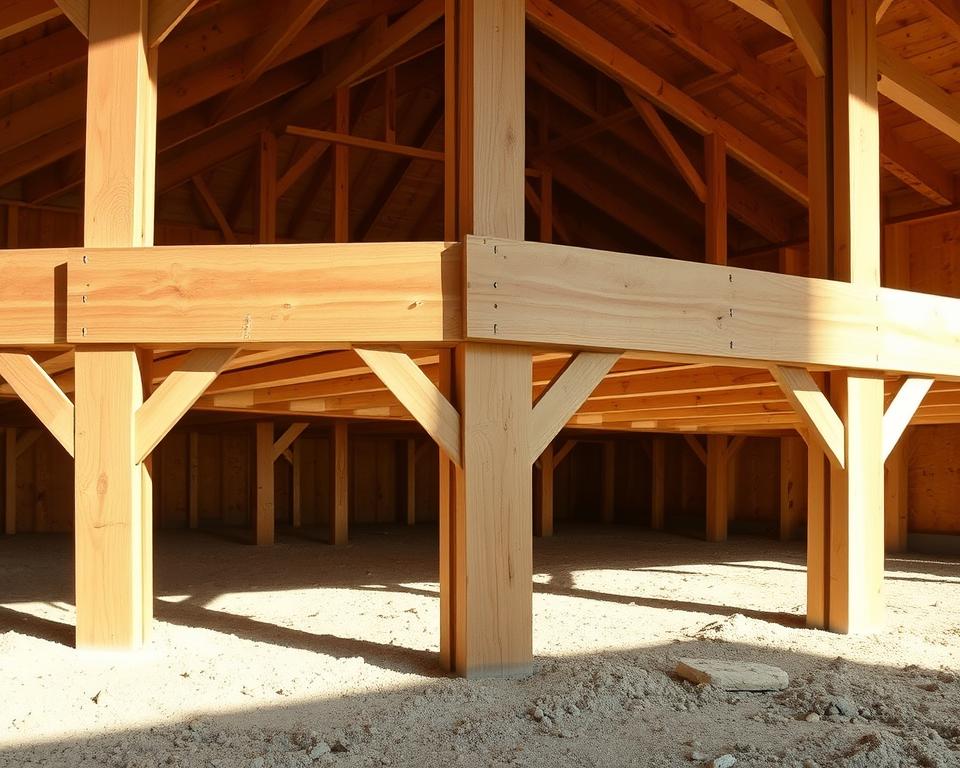

Creating a robust wooden shed foundation requires careful planning and precise execution. A timber frame base provides an excellent solution for uneven ground, offering flexibility and durability when constructed correctly.
Selecting the right pressure-treated lumber is crucial for building a long-lasting timber frame base. Choose high-quality wooden materials that can withstand moisture and ground contact. Pressure-treated lumber resists rot and insect damage, making it ideal for outdoor shed foundations.
- Inspect lumber for straightness and quality
- Select pressure-treated timber with appropriate thickness
- Check wood for potential structural defects
When constructing your timber frame base, follow these key steps:
- Clear the ground completely
- Create a level surface using gravel or sand
- Lay out pressure-treated lumber perimeter
- Ensure frame is perfectly square
- Secure frame with galvanised bolts
“A well-built wooden shed foundation determines the longevity of your entire structure.” – Professional Carpentry Magazine
Proper levelling techniques are essential for a stable timber frame base. Use a spirit level to check horizontal alignment at multiple points. Slight ground variations can be compensated by carefully adjusting timber placement and using supporting materials.
For optimal results, consider adding additional support beams across the wooden shed foundation. These cross-members distribute weight evenly and prevent potential warping or sagging over time.
Proper Drainage Solutions for Sloped Ground
Effective water management is critical when constructing a shed on uneven terrain. Drainage challenges can quickly compromise your shed’s foundation, leading to potential structural damage and costly repairs. Understanding how to implement robust shed drainage strategies will protect your investment and ensure long-term stability.

Water can be particularly destructive on sloped ground, creating multiple challenges for shed foundations. Proactive water management requires a strategic approach that addresses both surface and underground water movement.
Installing French Drains
French drains offer an exceptional solution for managing underground water flow. These ingenious drainage systems effectively redirect water away from critical areas, preventing moisture accumulation near your shed’s foundation.
- Dig a sloped trench away from the shed base
- Line the trench with landscape fabric
- Add perforated drainage pipes
- Cover with gravel for optimal water filtration
Surface Water Management
Controlling surface runoff requires careful planning and implementation of strategic techniques. Proper grading and strategic placement of gutters can significantly mitigate water-related risks to your shed.
- Create a gentle slope away from the shed foundation
- Install high-quality guttering systems
- Use downspout extensions to direct water further from the base
Preventing Water Damage
Implementing comprehensive water management strategies protects your shed from potential long-term damage. Proactive drainage solutions are always more cost-effective than reactive repairs.
Effective drainage is not just about managing water—it’s about preserving your investment.
Adding Stabilisation Methods
Dealing with uneven ground requires strategic foundation stabilisation techniques. Ground anchors provide an essential solution for securing shed bases in challenging terrain. These robust support systems ensure your structure remains stable and resistant to environmental pressures.
When confronting steep slopes or unstable ground, several key stabilisation methods can safeguard your shed’s structural integrity:
- Ground anchors: Deep-set metal rods that prevent shifting and movement
- Retaining walls: Structural barriers that create level surfaces and prevent soil erosion
- Reinforced foundation supports: Additional structural elements for enhanced stability
Retaining walls prove particularly effective for managing significant ground gradients. Professionally installed retaining walls can transform challenging landscapes into stable, usable spaces. These structures not only provide critical support but also create aesthetic landscaping opportunities.
Professional ground anchor installation involves precise techniques:
- Assess ground conditions thoroughly
- Select appropriate anchor type
- Install anchors at strategic depths
- Test anchor stability
- Secure foundation connections
Investing in proper foundation stabilisation methods protects your shed from potential structural damage, ensuring long-term durability and safety in even the most challenging terrains.
Conclusion
Building a shed base on uneven ground requires careful planning and precise execution. Your DIY foundation project can transform challenging terrain into a stable, long-lasting structure. By understanding site preparation techniques and implementing strategic uneven ground solutions, you’ve learned how to create a robust base that will support your garden shed for years to come.
The key steps in shed base construction involve thorough ground assessment, selecting appropriate foundation methods, and implementing proper drainage solutions. Whether you chose concrete blocks or a timber frame, your attention to detail will prevent future structural issues and ensure your shed remains level and secure.
For complex terrain or significant slope gradients, professional consultation might be recommended. Some landscape challenges require specialised expertise to guarantee optimal results. Your willingness to invest time and effort in creating a solid foundation demonstrates commitment to quality craftsmanship and long-term garden infrastructure.
Remember that a well-constructed shed base is more than just a support structure—it’s the foundation of your outdoor storage and workspace. With the skills you’ve gained, you’re now equipped to tackle challenging ground conditions and create a reliable, durable shed base that will serve you effectively.
FAQ
What tools do I need to build a shed base on uneven ground?
Essential tools include a laser level, spirit level, measuring tape, shovel, rake, wheelbarrow, string line, and pegs. You’ll also need safety equipment like gloves and protective eyewear. Specialised tools such as a transit level can help with more precise measurements on challenging terrain.
How do I determine the slope of my garden ground?
Use a spirit level and long straightedge to measure the gradient. Place the straightedge horizontally and measure the vertical drop over a set distance (typically every metre). A slope under 10cm per 3 metres is considered gentle, while anything steeper may require more complex levelling techniques.
Can I build a shed base on very steep ground?
While challenging, it’s possible with proper techniques. You might need to use retaining walls, stepped foundations, or ground anchors to create a stable base. In extremely difficult situations, consulting a professional landscaper is recommended to ensure structural integrity and safety.
What’s the best foundation type for uneven ground?
Concrete block foundations are typically most versatile for uneven terrain. They allow precise height adjustments and provide excellent stability. Timber frame bases can also work well for moderately uneven ground, offering flexibility and relatively easy installation.
How important is drainage when building a shed base?
Drainage is crucial to prevent water damage and foundation instability. Consider installing French drains, creating proper ground grading, and using gutter systems to redirect surface water. Poor drainage can lead to moisture problems, foundation shifting, and potential structural damage to your shed.
How do I level concrete blocks on a sloped surface?
Start by establishing the lowest point as your reference. Use gravel or sand to build up lower areas, ensuring each block is perfectly level using a spirit level. Adjust block heights incrementally, checking alignment both horizontally and diagonally to create a stable, even surface.
What soil types are most challenging for shed base construction?
Clay soils and waterlogged ground present the most significant challenges. These soil types can become unstable, expand, and contract with moisture changes. Sandy or gravelly soils typically provide better drainage and more stable foundation conditions.
How much ground preparation is typically required?
Thorough ground preparation is essential. This includes clearing vegetation, removing rocks and debris, checking for underground utilities, and creating a level surface. Depending on your terrain, this might involve excavation, grading, and adding hardcore or gravel as a base layer.
Can I build a shed base without professional help?
Many DIY enthusiasts can successfully build a shed base with careful planning and the right techniques. However, if you’re dealing with extremely challenging terrain, significant slopes, or complex drainage issues, consulting a professional landscaper or contractor is advisable.
How do I protect my shed base from moisture and ground movement?
Use damp-proof membranes, ensure proper drainage, choose pressure-treated timber or rot-resistant materials, and consider using ground anchors. Regular maintenance and inspecting the base annually can help prevent long-term issues with moisture and ground instability.

