Building a Shed Base: A Step-by-Step Guide

Every successful garden structure begins from the ground up. The foundation is the most critical part of the entire construction. A firm and level platform ensures the shed stands straight and functions correctly for years.
Without this solid groundwork, assembly becomes a struggle. Screw holes may not align, and doors might not fit their frames properly. These issues compromise the structural integrity and reduce the service life of the building.
A well-constructed base does more than just support the weight. It prevents rot by stopping groundwater from seeping into the timber bearers. This protection is vital for the longevity of any outdoor storage solution.
This guide explores various foundation options suitable for UK gardens. It covers timber frames, plastic grids, paving slabs, and concrete foundations. Each method offers a durable solution to create a stable platform.
Proper installation protects against subsidence and water damage. It ensures the shed remains a valuable and lasting addition to any garden. Following these steps will lead to a successful and professional-looking result.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Key Takeaways
- A level foundation is essential for correct assembly and structural stability.
- Proper groundwork prevents doors and windows from becoming misaligned.
- A solid base significantly extends the lifespan of the garden building.
- It protects the structure from ground moisture, preventing rot and decay.
- Choosing the right base type is crucial for the specific garden conditions.
- A well-built foundation safeguards your investment against future problems.
Introduction to Building a Shed Base
A shed’s ability to withstand the British climate and remain structurally sound hinges on its base. This initial stage is not merely about support; it is about creating a permanent, stable environment for the entire structure.
Overview and Importance of a Solid Base
Installing a garden building on an uneven surface causes the timbers to flex. This movement leads to misaligned screw holes and joints during construction. Once assembled, doors and windows may not close correctly.
A sturdy, level foundation prevents this structural flexing. It ensures all components fit together perfectly from the start. This correct installation is crucial for long-term stability.
Using floor bearers to raise the shed slightly above the base is a key technique. This small gap allows air to circulate freely underneath. This ventilation is vital for protecting the wood from dampness and rot.
Benefits of a Level, Durable Foundation
The primary benefit of a well-constructed foundation is the prevention of subsidence. A solid base stops the shed from sinking over time, which directly extends its lifespan. This protects your investment against future problems.
Furthermore, a durable platform acts as a barrier against groundwater. It stops moisture from seeping into the timber bearers, which is a primary cause of deterioration. This protection is essential for longevity.
| Potential Issue | Consequence | Solution Provided by a Proper Base |
|---|---|---|
| Uneven Ground | Structural flexing, misaligned doors/windows | Creates a perfectly level surface for assembly |
| Ground Moisture | Wood rot and decay | Raises the floor for air circulation and acts as a damp-proof barrier |
| Soil Subsidence | Shed sinks, causing structural stress | Provides a stable, non-shifting platform that distributes weight evenly |
Whether using timber, plastic, paving, or concrete, the principle remains constant. A level and solid foundation is non-negotiable for a successful installation. It is the cornerstone of a durable garden building.
Planning and Preparing the Ground for Your Shed
Before any construction begins, thoughtful planning ensures the final result meets both practical and aesthetic needs. Four key factors demand consideration: location, intended purpose, sunlight direction, and drainage capabilities. The chosen area must serve the shed’s function while receiving appropriate light exposure.
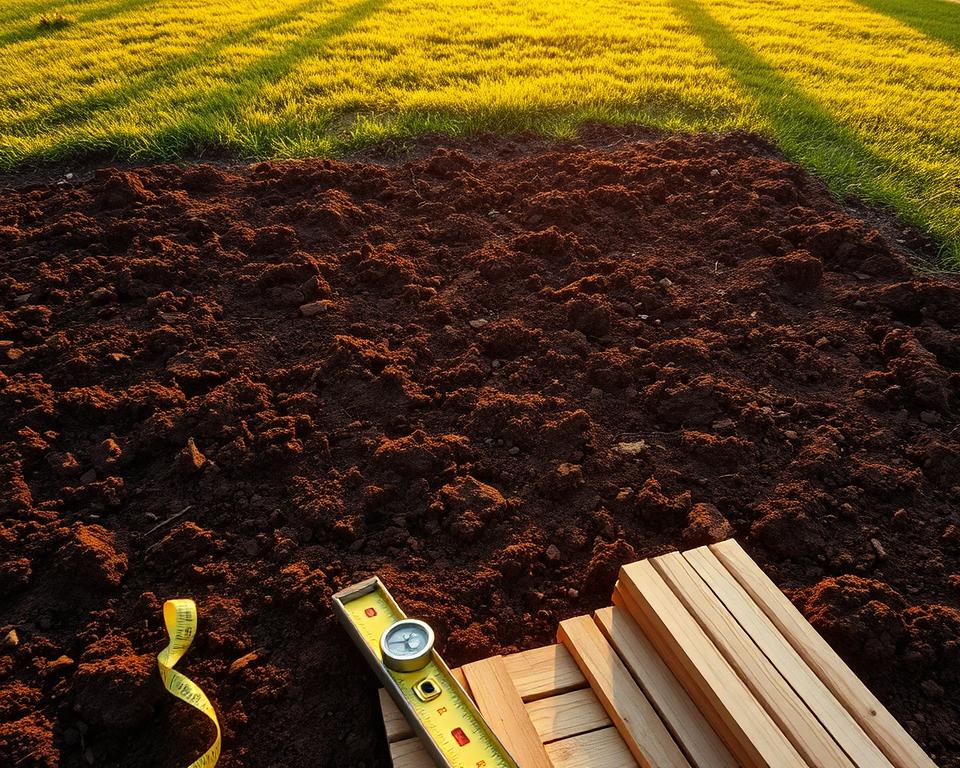

Site Clearance and Measurement
Begin by clearing the selected ground of all vegetation, including grass and weeds. This creates a clean working surface. Next, measure the shed dimensions precisely to determine the required base size.
Use stakes and string to mark the perimeter accurately. This visual guide helps maintain proper proportions. Leave approximately 90cm of space around the planned structure for construction access and future maintenance.
Ground Levelling and Drainage Considerations
A level surface is crucial for stability. Remove high spots and fill low areas to create an even plane. Check the ground using appropriate tools to confirm it’s perfectly flat.
Proper drainage prevents water accumulation around the structure. Assess natural water flow and consider creating a slight slope away from the shed. This simple measure protects against moisture damage over time.
Materials and Tools Required for a Shed Base
Gathering the correct materials and tools before starting is fundamental to a successful project. The specific items needed depend entirely on the chosen foundation type. Having everything on hand streamlines the entire process.
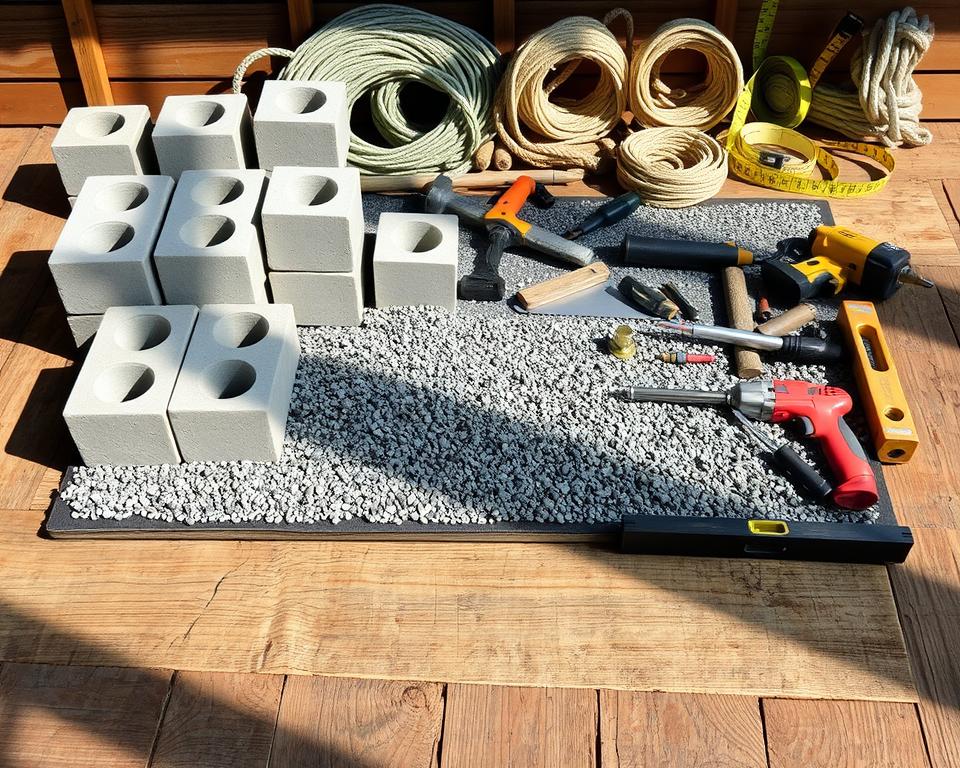

Essential Materials Overview
Each base type requires distinct core materials. A timber frame needs a kit with fixings and pressure-treated wood. Plastic grids come as interlocking kits, often needing gravel for infill.
For a paving slab or concrete foundation, key components include slabs, sharp sand, and cement. Metal components like galvanised screws and brackets are vital for durability against the elements.
Supplementary items play a crucial role. Pea gravel aids drainage, while cement binds concrete mixtures. These additional materials ensure a robust and long-lasting result.
Key Tools for Precise Installation
Accuracy is paramount. A long spirit level, tape measure, and square are non-negotiable for ensuring a perfectly level base. Basic tools like a spade and club hammer are essential for ground preparation.
Some tools are specific to the method. A power drill with specialist bits is needed for assembling a timber frame. An edging iron creates clean lines, while a vibrating plate compactor is ideal for compacting concrete sub-bases.
It is wise to hire specialised equipment, like compactors, for a one-time project. This approach is cost-effective and guarantees professional-grade compaction.
Building a Shed Base: A Step-by-Step Guide
The correct assembly of any garden building relies heavily on the initial stages of its construction. This part of the guide provides a clear, methodical process. It covers everything from planning to the final touches for various foundation types.
Every kit and design can have unique requirements. That is why it is critical to follow the manufacturer’s specific instructions for your timber frame and floor. Even a comprehensive general guide cannot replace these tailored details.
Adhering to Manufacturer Instructions
Assembly instructions differ significantly between products. Ignoring specific guidelines can lead to improper installation. This mistake might void warranties or cause structural issues later.
Always take the time to read the manual thoroughly before starting. This preparation prevents errors and ensures a smooth construction process. It is the first and most crucial step.
Ensuring a Perfect Fit for Your Shed
Achieving the right fit is about more than just dimensions. The foundation must be precisely sized to support the structure correctly. The recommended approach is to make the foundation either exactly the same size as the building’s footprint.
Alternatively, it can be crafted to be 25 millimetres smaller on every side. This slight difference creates a subtle overhang. The overhang is a simple yet effective feature.
It stops rainwater from pooling directly against the timber floor and runners. In the UK’s damp climate, this detail is vital for preventing rot. It significantly extends the life of the garden building.
Once the foundation is perfectly level and sized, the shed floor can often be placed directly on top. Frequently, no screws or fixings into the foundation are necessary, allowing for natural settlement.
| Foundation Size | Best Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Same as shed footprint | Maximises interior space; ideal on very level ground | Provides full support across the entire floor area |
| 25mm smaller on all sides | All climates, especially wet regions | Creates a water-shedding overhang to protect timber |
Rushing this process can lead to misalignment and future problems. Each step must be executed with care to ensure a durable and professional result. This careful approach guarantees the sturdiness of the final construction.
Timber, Plastic, Paving, and Concrete Base Options
Selecting the appropriate foundation is the first critical decision in creating a durable outdoor structure. Homeowners have four main material choices, each with distinct installation methods and benefits.
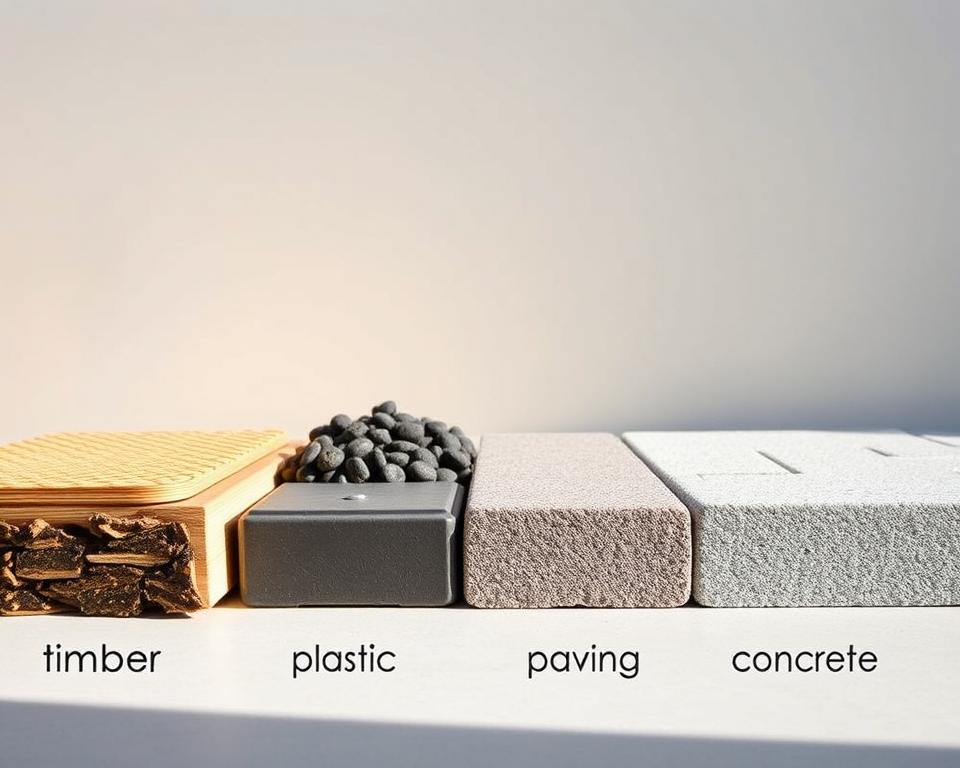

Timber Shed Base (Portabase) Installation
A timber base, often called a Portabase, uses pressure-treated wood with metal spikes. These spikes hammer into the ground for stability. This type elevates the shed floor, allowing air circulation that reduces rot risk.
It works well on level lawns. For a patio installation, metal L-shaped legs support the frame. The design keeps the structure securely in place.
Installation of Plastic and Paving Slab Bases
Plastic grids offer a quick, eco-friendly option. Made from recycled materials, they interlock to form a free-draining platform. A top dressing of sharp sand helps bed them in securely.
Paving slabs require a 5cm compacted hardcore sub-base. The total excavation depth is about 12cm when level with the ground. This method provides excellent durability.
Constructing a Concrete Base for Longevity
A concrete foundation is the most permanent solution. It needs 7.5cm of hardcore beneath 7.5cm of concrete. The total depth reaches approximately 15cm.
This type requires proper curing time before use. The substantial layer ensures maximum load-bearing capacity and longevity for heavy structures.
| Base Type | Installation Time | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Timber | Quick | Cost-effective with good ventilation |
| Plastic | Fastest | Excellent drainage and eco-friendly |
| Paving Slabs | Moderate | Durable yet relatively easy to install |
| Concrete | Longest (requires curing) | Maximum durability and stability |
Key Techniques for Ensuring a Level and Durable Base
Precision in foundation work separates amateur installations from professional results. The techniques used during this phase determine the structure’s long-term stability and performance.
Using a Spirit Level for Accurate Alignment
A spirit level is indispensable for creating a perfectly flat surface. Users should check and re-check the level at multiple points across the frame. This continuous verification prevents minor errors from becoming major issues.
After establishing the initial level, verify each corner with a builder’s square. Ensure all four corners form perfect 90-degree angles. For final confirmation, measure diagonally between opposite corners. Identical measurements confirm the frame is perfectly square.

Securing the Base with Effective Methods
Once positioned correctly, secure the base firmly. For timber frames, hammer metal spikes at each corner. Use screws to attach L-shaped bracket feet to the inside of the frame. Position these feet so the structure remains stable in all directions.
Continue checking the level during the securing process. Even slight tipping can cause long-term damage. Use stakes and string to maintain alignment. Address any uneven sections immediately by adding supporting material.
Essential Safety and Maintenance Checks
The longevity of outdoor buildings depends not only on proper installation but also on consistent safety practices and upkeep. These measures protect both the installer and the investment over time.
Personal Protective Equipment and Safety Measures
Always wear appropriate protective gear during construction. Essential items include rigger gloves for handling timber, safety goggles, dust masks, and sturdy footwear.
When working with treated wood, wash hands thoroughly before eating. Chemicals in the treatment process require careful handling. Cement work demands extra caution – wet cement can cause burns.

Weather conditions significantly impact the work. If rain threatens, cover the base with tarpaulin. For concrete in warm weather, use damp sacks and sprinkle with water over 24 hours to prevent cracking.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection Tips
Plan for future access during initial installation. Leave adequate space around the shed walls for maintenance work. This allows for painting or treating the wood when needed.
Regular checks should include inspecting for water damage and ensuring the base remains level. Make sure drainage systems continue functioning properly over time. Proper access makes these tasks much simpler.
Additional Considerations for Shed Base Installation in the UK
Finalising the ideal location for a garden structure involves more than just measuring the ground. Several UK-specific factors require attention before construction commences.
Planning Permission and Local Regulations
In most cases, a garden shed is considered a temporary structure. This classification means planning permission is often not required. Important exceptions exist, particularly within conservation areas.
Specific rules regarding size and height can vary. It is essential to consult the Government’s Planning Portal for the most current legislation applicable to your local area.
If you plan to install electrical supply, consult a qualified electrician before finalising the base’s location. This foresight ensures the installation meets all safety standards.

Access, Sunlight, and Environmental Factors
Consider the intended purpose of the structure. A tool storage unit is best placed near the growing space for convenience. Think about the required amount of natural light.
While sunlight is beneficial, direct exposure can cause overheating. The ideal spot maximises light while minimising potential dampness inside.
Good drainage is crucial to prevent water from pooling. Ensure the base is not built too close to walls or fencing. Sufficient access on all sides is necessary for construction and future maintenance.
- Access: Allow space for painting and treating the timber.
- Sunlight: Balance natural light with the risk of overheating.
- Drainage: A slight slope away from the structure aids water runoff.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the success of any garden structure is determined by the quality of its foundation. This guide has detailed the necessary steps to create a robust and level platform. A well-constructed base is not just a support; it is the critical element that ensures longevity and stability.
Investing proper time and effort at this initial step prevents future issues like misaligned doors and structural damage. Whether opting for paving, concrete, timber, or plastic, the principles of good preparation remain constant.
Attention to detail, from ensuring a perfectly flat surface to securing the corners, guarantees a professional result. This careful approach protects your investment and ensures your garden building stands the test of time.
Armed with this guide, you can confidently approach your project. Remember, a sturdy shed is a direct result of the solid foundation upon which it is built.
FAQ
Do I need planning permission to build a shed base?
In most cases, a shed base does not require planning permission if the shed itself falls under ‘permitted development’. However, rules vary. One should check with their local council if the shed is large, placed forward of the house, or if they live in a conservation area.
What is the best type of base for a garden shed?
The best option depends on the shed’s size, weight, and the garden’s ground. Concrete offers maximum durability and stability. Paving slabs are a solid, easier alternative. Timber or plastic bases provide good ventilation and are simpler to install on reasonably level ground.
How do I ensure my shed base is perfectly level?
Use a long spirit level and a straight-edged piece of timber. Check across the surface in multiple directions. For a concrete base, a screed board helps create a flat finish. Accurate levelling at this stage prevents future issues with the shed’s doors and walls.
Can I build a shed base on uneven ground?
Yes, but the ground must be levelled first. This may involve removing turf and topsoil, then compacting a hardcore sub-base. Building on a slope requires significant excavation or constructing a retaining frame to create a level construction area.
How deep should a concrete shed base be?
A concrete base should typically be at least 75mm to 100mm deep. For larger sheds or softer ground, a depth of 100mm to 150mm is advisable. It must be laid on a compacted hardcore sub-base of around 50mm to 75mm for proper support and drainage.
Is drainage important for a shed base?
Absolutely. Proper drainage prevents water from pooling under the shed, which can cause dampness and rot in timber floors. A slight slope away from the shed or a free-draining material like gravel around the base’s perimeter aids water run-off.
What safety equipment is needed when building a base?
Essential personal protective equipment includes sturdy gloves, safety goggles, and steel-toe-capped boots. When mixing concrete or cutting materials, a dust mask is also recommended to protect against fine particles.

